SINDBAD info Structure
The info structure serves as the central information hub for SINDBAD experiments. During experiment initialization, the SINDBAD preprocessor parses configuration settings and consolidates them into a comprehensive NamedTuple named info that ensures consistency and type stability from input through model simulation to output.
Reserved Variable
The info variable name is strictly reserved within SINDBAD and plays a critical role in the model execution and stability. Users must not overwrite or modify this variable.
Purpose and Functionality
The info structure acts as the central nervous system of a SINDBAD experiment, containing all necessary information for:
Data ingestion and processing
Model initialization and execution
ParameterOptimization configuration
Output generation and analysis
Structure Overview
The info structure is organized into six main branches:
1. Experiment Configuration (experiment)
Contains experiment metadata and file paths:
Basic information: name, domain, version, user, execution date
Configuration file paths
settings for input data
2. Terrestrial Ecosystem Model (models)
Stores model-specific information:
Model processes
Spinup model selection
parameters of the model structure
3. Simulation Output (output)
Stores information related to output
output format and directories
output variables
4. Model Spinup (spinup)
Information on how to do model spinup
a path to restart file, if given
sequence of spinup steps
5. Model helpers (helpers)
Intermediary helper objects necessary for model run and type stability
dates and time steps needed for temporal aggregation
initial instantiation of SINDBAD
landnumbers for selected
typeand numerical or mass-balance toleranceruntime options and information of experiment
6. ParameterOptimization Settings (optimization)
Available when parameter estimation or model cost calculation is enabled:
ParameterOptimization algorithm settings (
optimizer)Sensitivity analysis settings, when needed/set in
optimization.json(sensitivity_analysis)Cost function configuration (
cost_options)Parameter table with optimization parameters and their information
Options for running optimization (
run_options)
7. Hybrid Modeling (hybrid)
The hybrid field in the info structure contains all configuration and runtime information related to hybrid (process-based + machine learning) modeling in SINDBAD. This field is present when hybrid or machine learning components are enabled in the experiment configuration through the passing of hybrid configuration file in experiment.basics.config_files.
info.hybrid is a NamedTuple that holds various subfields, each representing different aspects of the hybrid modeling setup. It includes:
ml_model: Settings for the machine learning model (e.g., architecture, activation functions, number of layers/neurons, random seed).ml_training: Training configuration, such as method, batch size, number of epochs, loss function, data split ratios, and fold information for cross-validation.ml_gradient: Gradient computation method and options (e.g., which AD or finite difference library to use, chunk size).ml_optimizer: Optimizer settings for training theMachine Learningmodel (e.g., optimizer type, learning rate, momentum parameters).covariates: Information about covariate data used asMachine Learningfeatures (e.g., file path, variables to use).replace_value_for_gradient: Value to use for missing or masked data during gradient computation.save_checkpoint: Boolean flag indicating whether to save model checkpoints during training.random_seed: Seed for reproducibility ofMachine Learningtraining and data splits.
This field is automatically populated by the SINDBAD preprocessor based on the relevant sections of your experiment's JSON configuration files (such as parameter_learning.json in example for hybrid modeling).
Example usage:
AccessMachine Learningmodel settings:
info.hybrid.ml_modelGet training options:
info.hybrid.ml_training.optionsRetrieve optimizer configuration:
info.hybrid.ml_optimizer.optionsAccess covariate file path:
info.hybrid.covariates.path
Interactive Exploration of SINDBAD info
Interactively view an example info from a SINDBAD experiment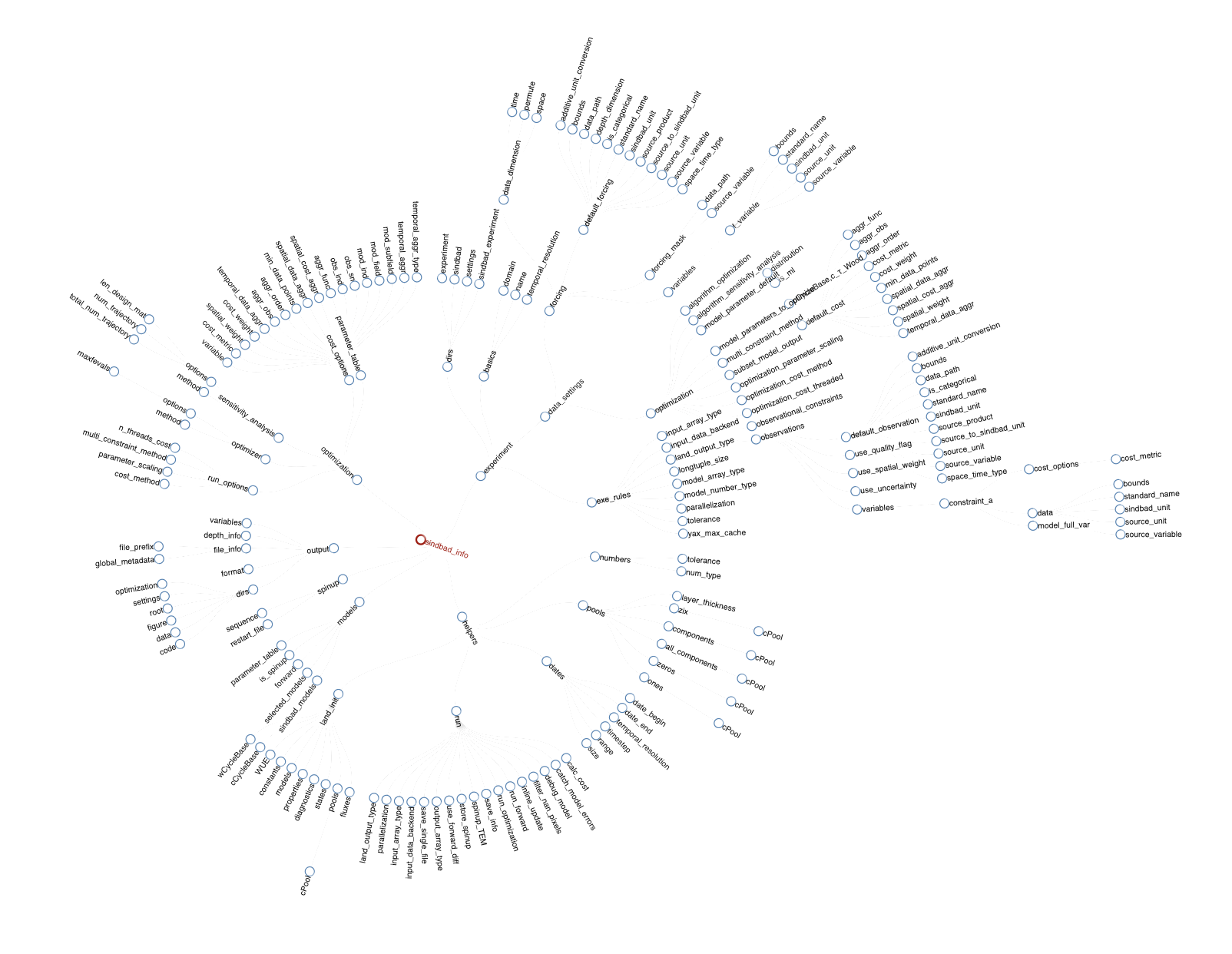
Usage Guidelines
Access information using dot notation (e.g.,
info.experiment.name)Refer to specific fields when configuring model components
Use the structure to track experiment settings and state and cross check if the json settings are correctly parsed and consolidated
Maintain consistency with configuration files